几何的隐式表示与显示表示
Many Ways to Represent Geometry
Implicit 隐式表示
- algebraic surface
- level sets
- distance functions
- …
Explicit 显示表示
- point cloud
- polygon mesh
- subdivision, NURBS
- …
Each choice best suited to a different task/type of geometry
Implicit 隐式表示
隐式表示就是告诉我们点满足某种特定的关系,而不是告诉我们点具体在哪。
More Implicit Representations in Computer Graphics
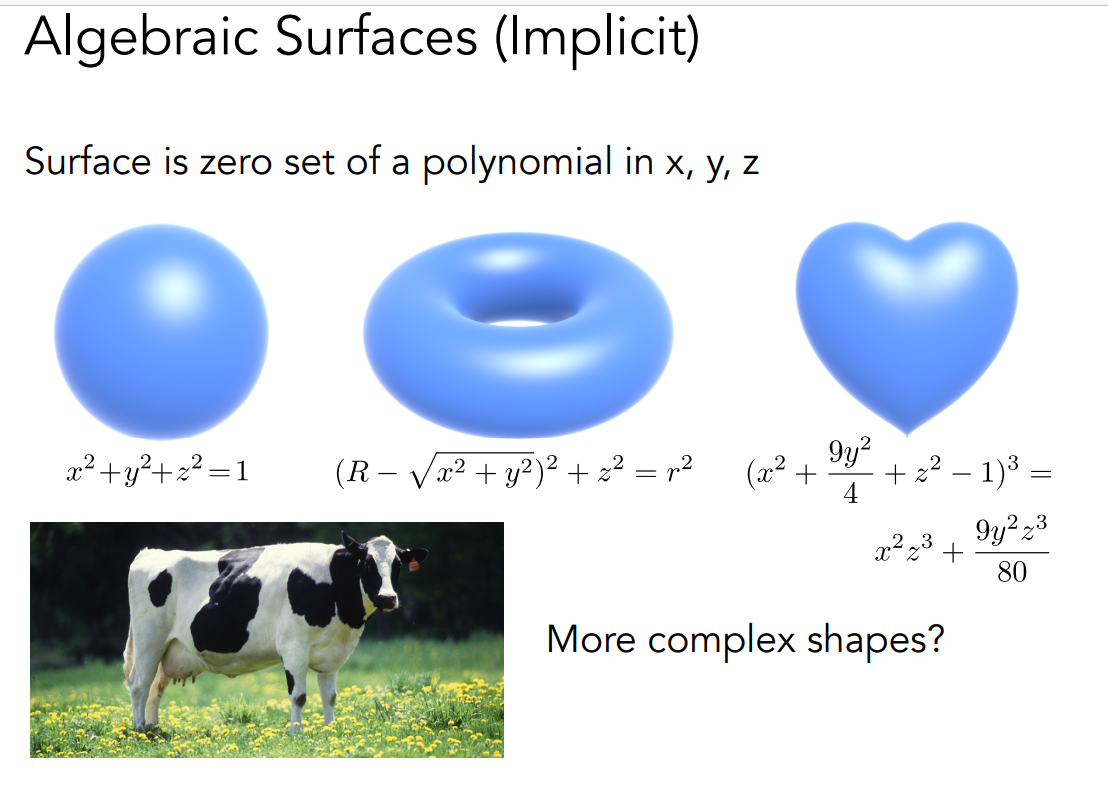
Algebraic Surfaces
直接用数学公式表示,最大的问题是不直观,比如右边的心形很难直观的想出来,而更复杂的情况就很难表示,比如下面的奶牛就很难用公式表示出来。
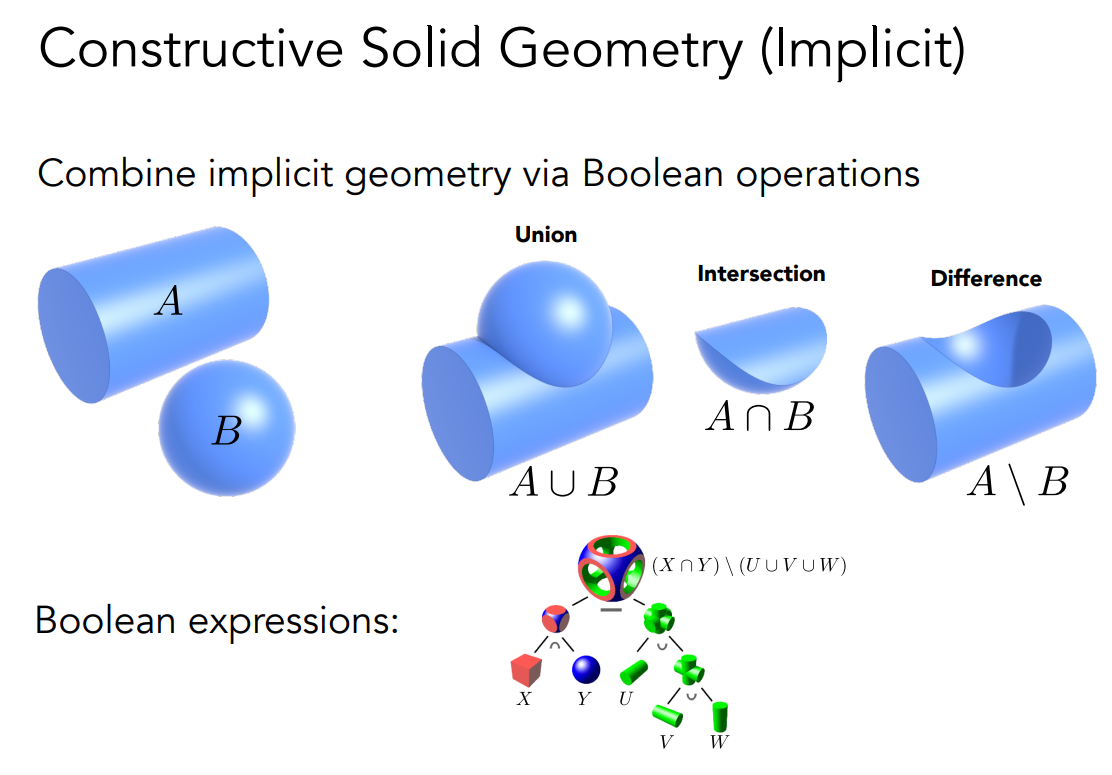
Constructive Solid Geometry
通过一系列基本几何的基本运算来定义新的几何。
比如下面圆柱A、球B就是基本几何,通过类似于集合的交、并、差运算,就可以形成新的几何。
Distance Functions
不直接描述几何的表面,而是描述空间中任意一个点到物体表面的最小距离。
物体内距离为负,物体表面距离为零,物体外距离为正。

可以将两个距离函数做blending,得到一个新的几何物体。

距离函数的表示能力非常强,比如下图的例子,它将物体之间的联系圆滑的过度过去。

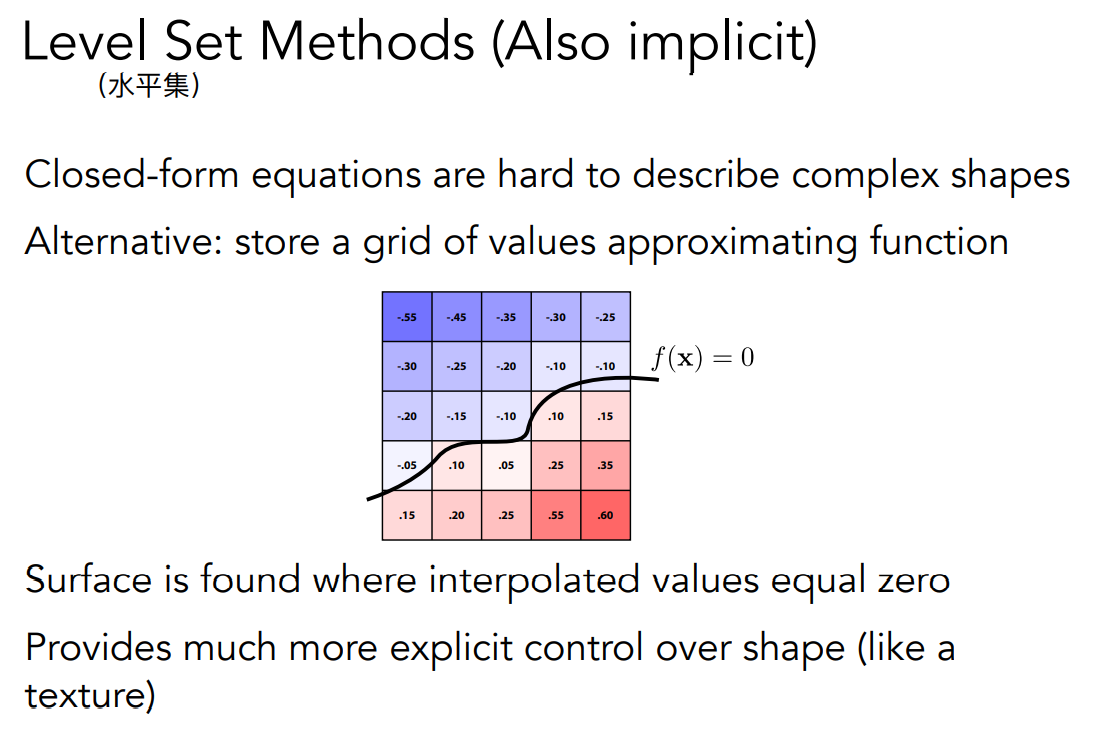
Level Set Methods
如果距离函数不方便写成解析的形式,还可以通过水平集的方法表示出来。水平集和上面距离函数的区别仅仅是表示形式的区别。
可以通过双线性插值等方法,得到$f(x)=0$的位置。
地理上的等高线和水平集比较类似,一条等高线就是$f(x)$等于某个高度的地方。
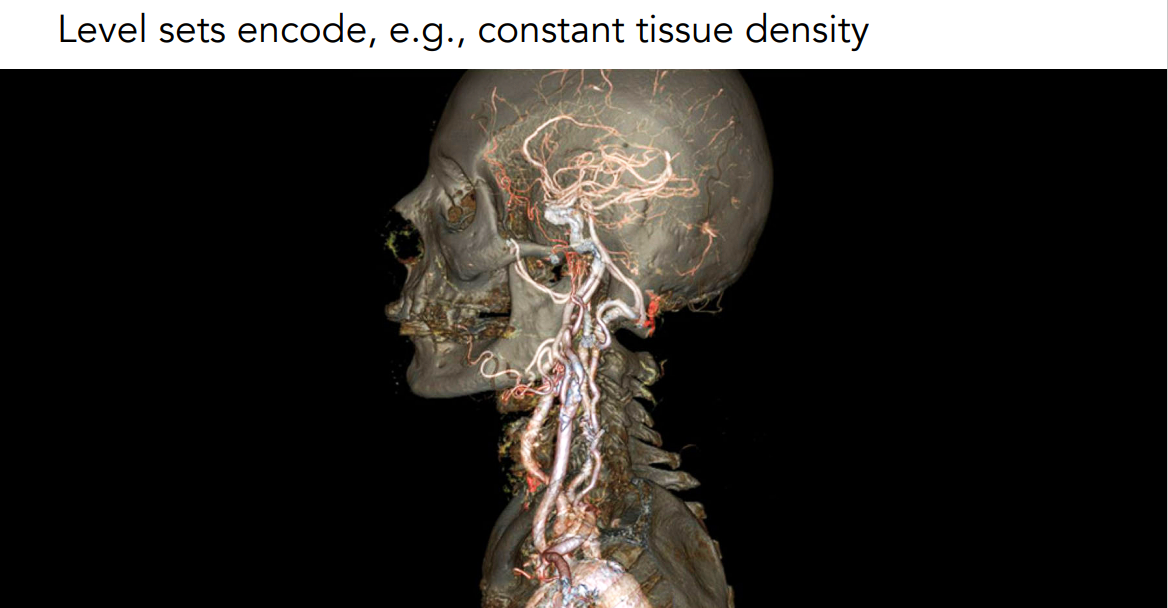
水平集不一定要定义在二维的格子上,也可以定义在三维的格子上,下面就是一个例子。
水平集根据组织密度,构成了三维体积模型。
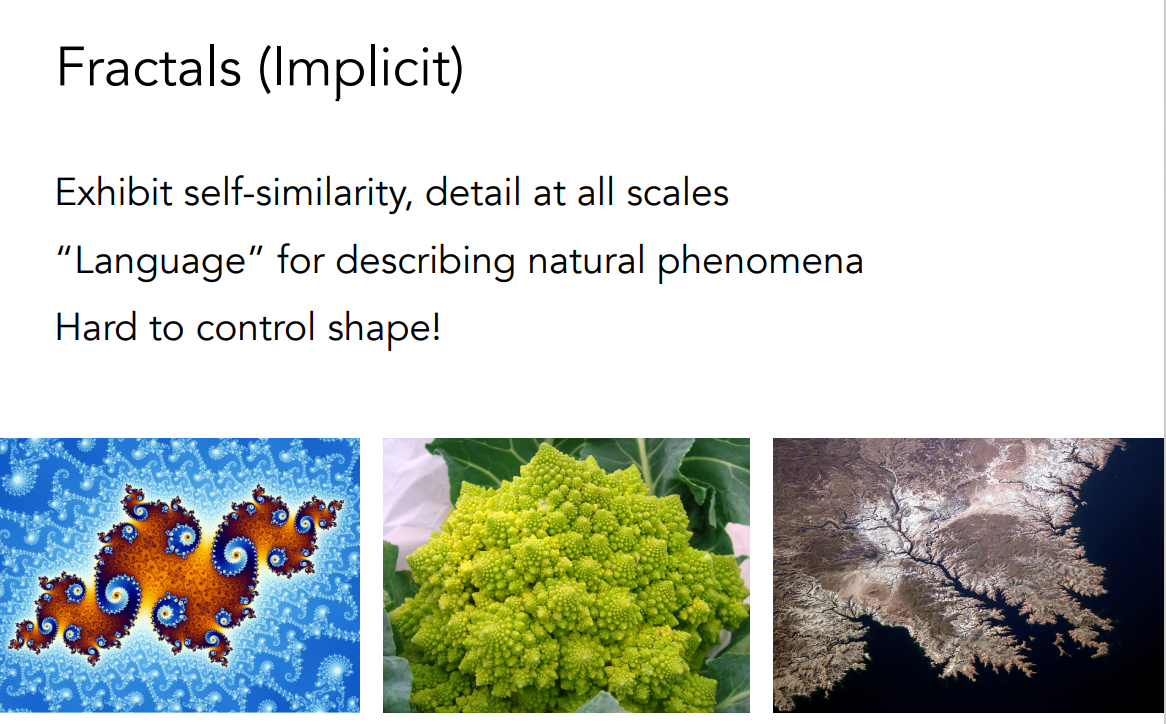
Fractals
几何还有一种特殊的方法,叫做fractal(分形)。
分形是一个自相似的过程,包括在不同的尺寸上,指的是自己的一个部分和它的整体长得非常像,类似于递归。
Pros & Cons
Pros:
compact description (e.g., a function)
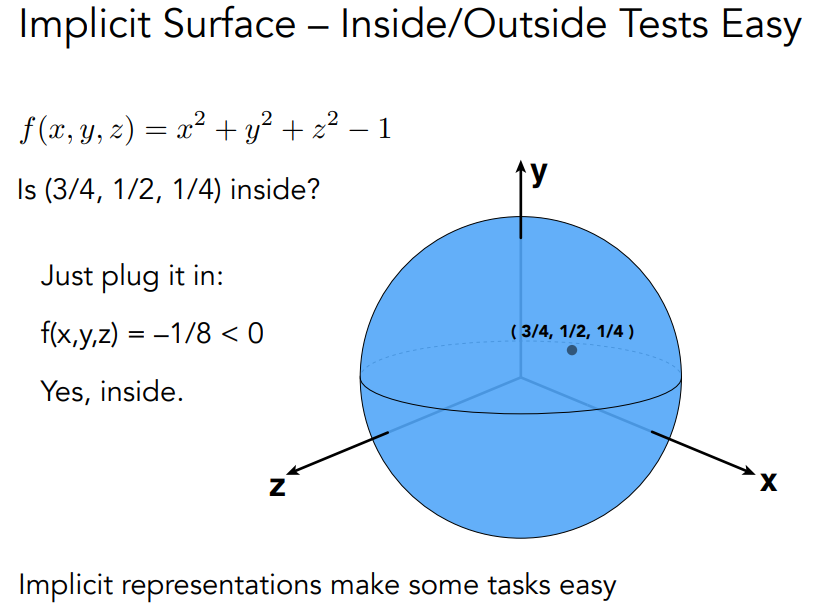
certain queries easy (inside object, distance to surface)
将点代入$f(x,y,z)$,如果小于零在里面,大于零在外面,等于零在面上。例如下面这个例子:
good for ray-to-surface intersection (more later)
for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error
easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid)
Cons:
difficult to model complex shapes
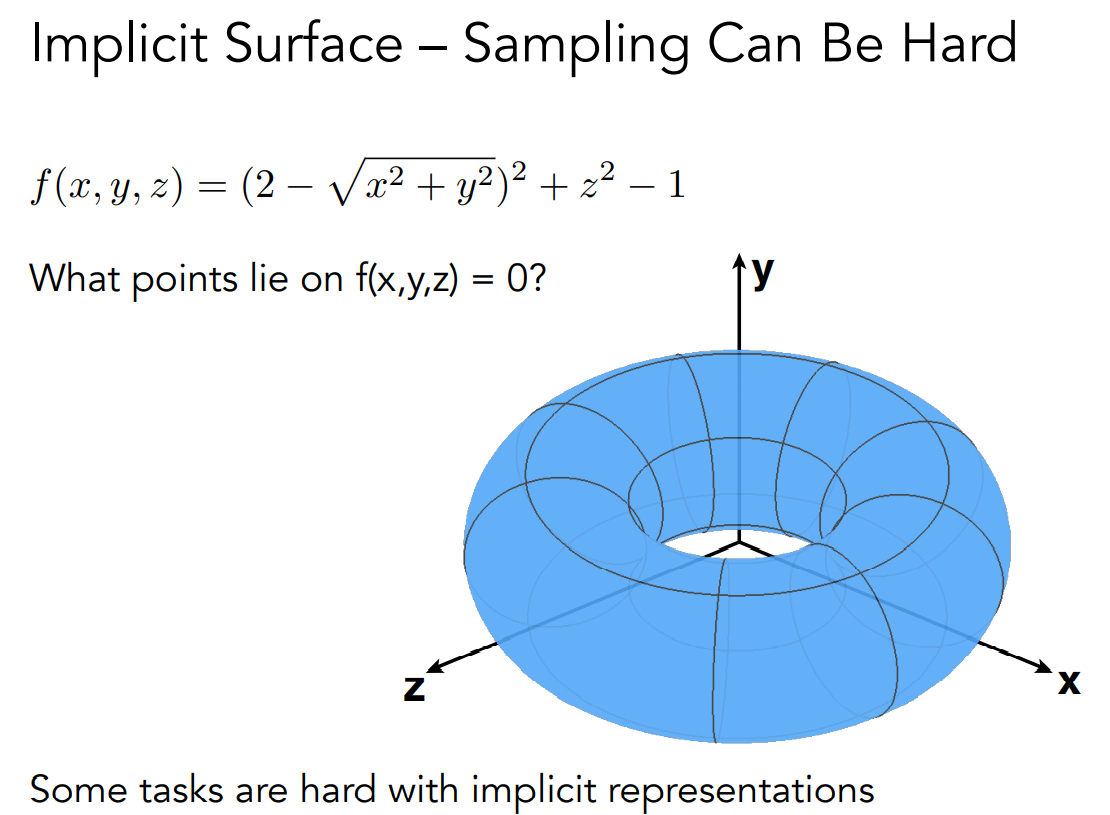
sampling can be hard
Explicit 显示表示
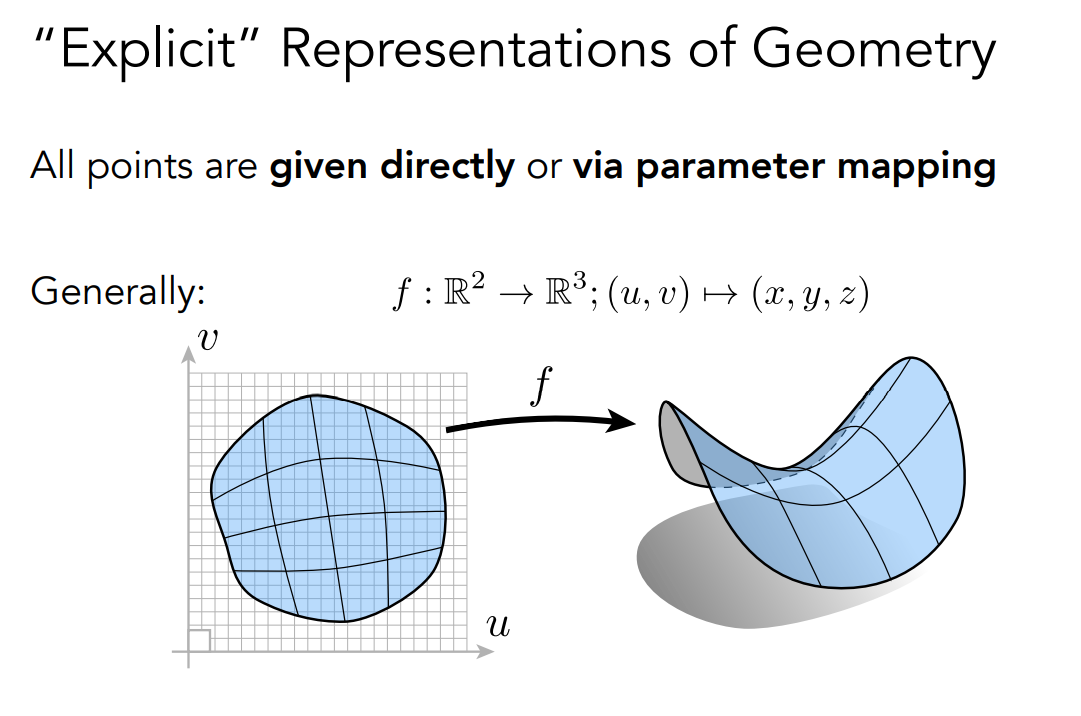
显示表示指的是直接给出所有的点,或者通过参数映射给出所有的点。下图是通过参数映射表示点的例子。
Many Explicit Representations in Graphics
Point Cloud
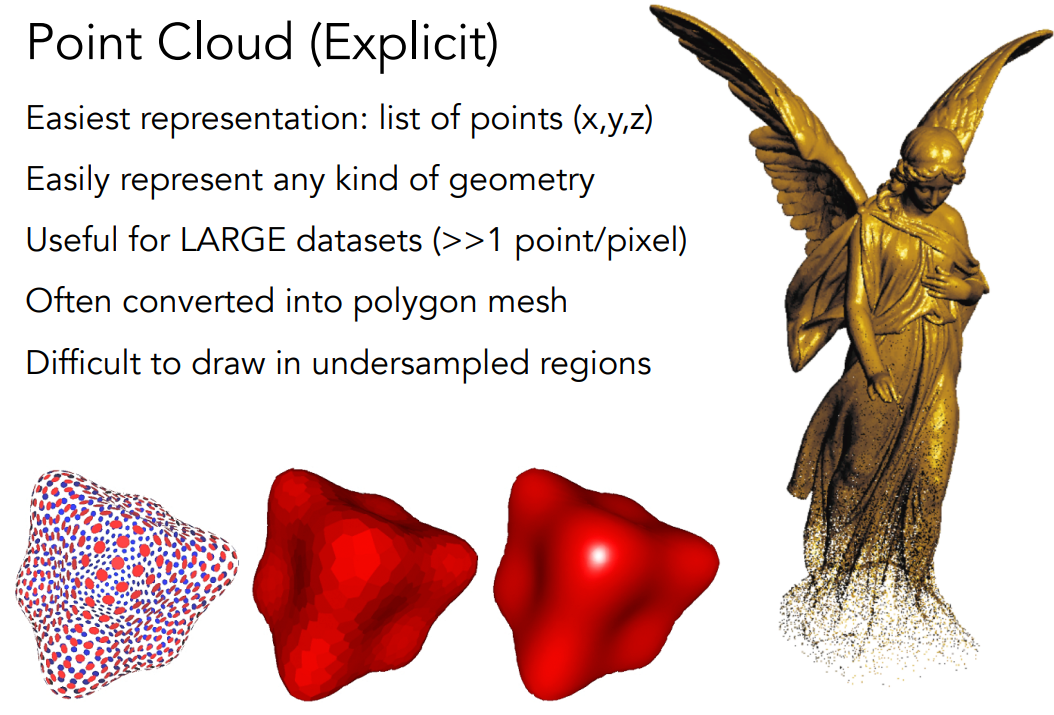
Polygon Mesh
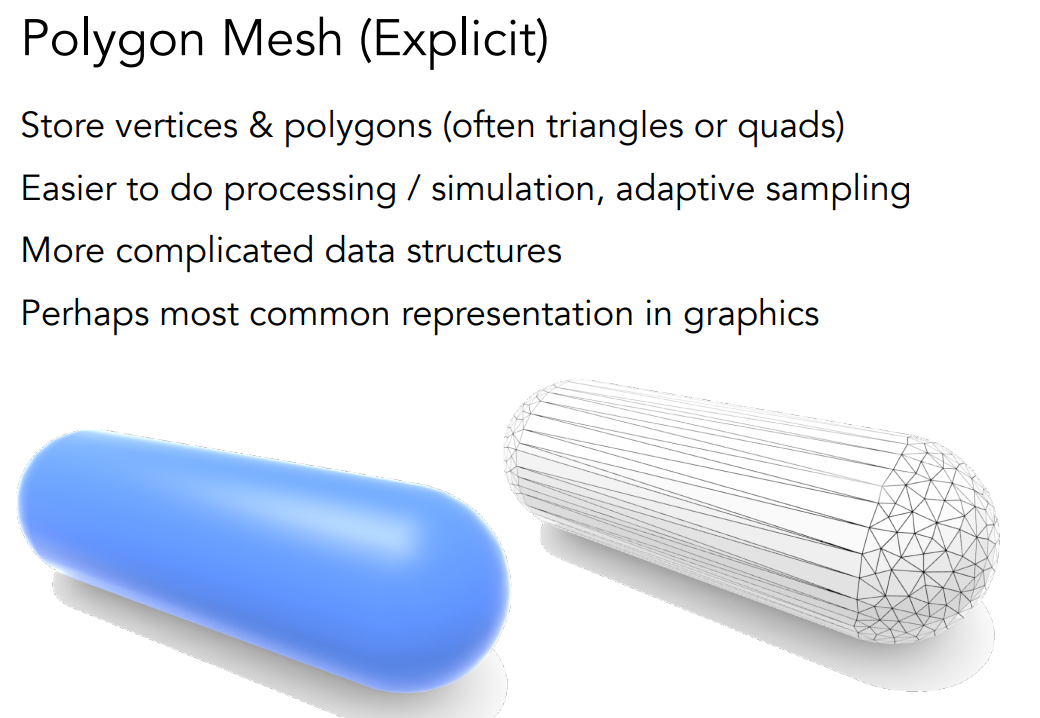
The Wavefront Object File (.obj) Forma
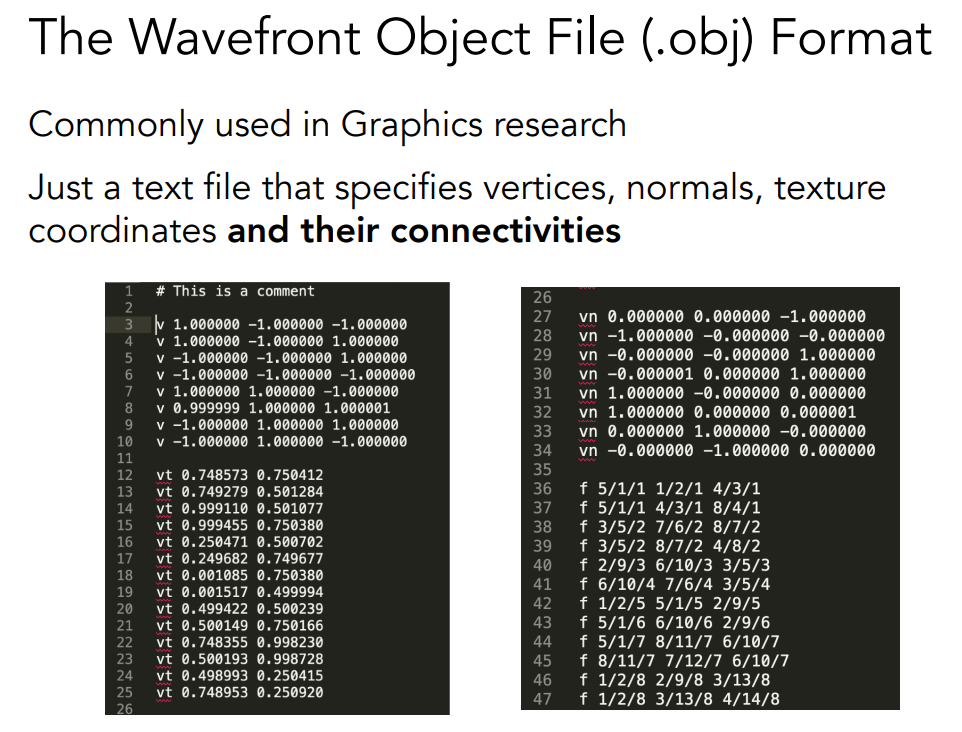
Pros & Cons
Pros:
采样很简单,将所有的UV代入就能得到所有的点了
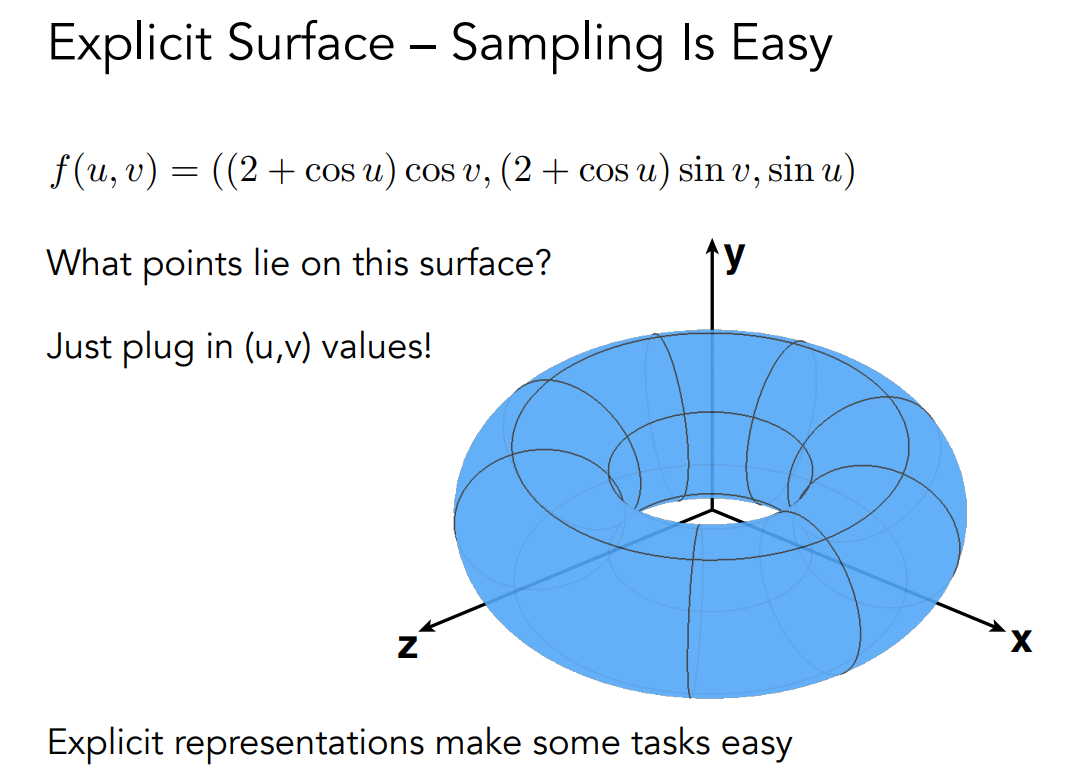
Cons:
判断点在表面的里面还是外面很困难
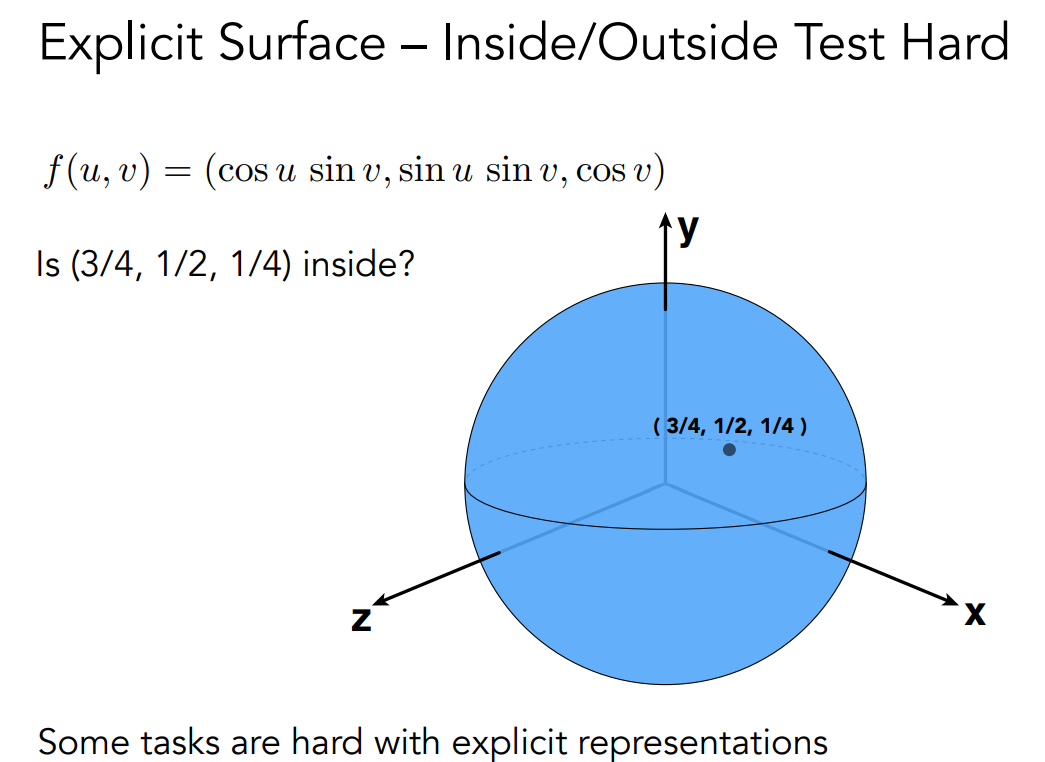
思考
- 在隐式表示Constructive Solid Geometry部分,这些运算如何使用解析的形式表示出来?如果基本几何之间只使用一部分做运算(两个基本几何的中心不对齐),又怎么表示?
- 在显示表示中,可以通过映射表示几何物体,比如$f(u, v) = ((2 + cos u) cos v,(2 + cos u) sin v,sin u)$就表示了一个圆环,这样从二维向三维映射的方式能够表示所有的几何物体吗?如果是一头奶牛,可以使用$f(u,v)$的映射表示吗?如果圆环的位置移动了,或者姿态改变了,还可以通过二维向三维的映射表示吗?(也许可以先计算几何当前位置到某个“标准位置”的映射关系,即三维到三维的映射,然后把这个映射再反馈到二维到三维的映射中?这应该只是一个线性的变换???)



