FLARE: Feed-forward Geometry, Appearance and Camera Estimation from Uncalibrated Sparse Views
Motivation & Contributions
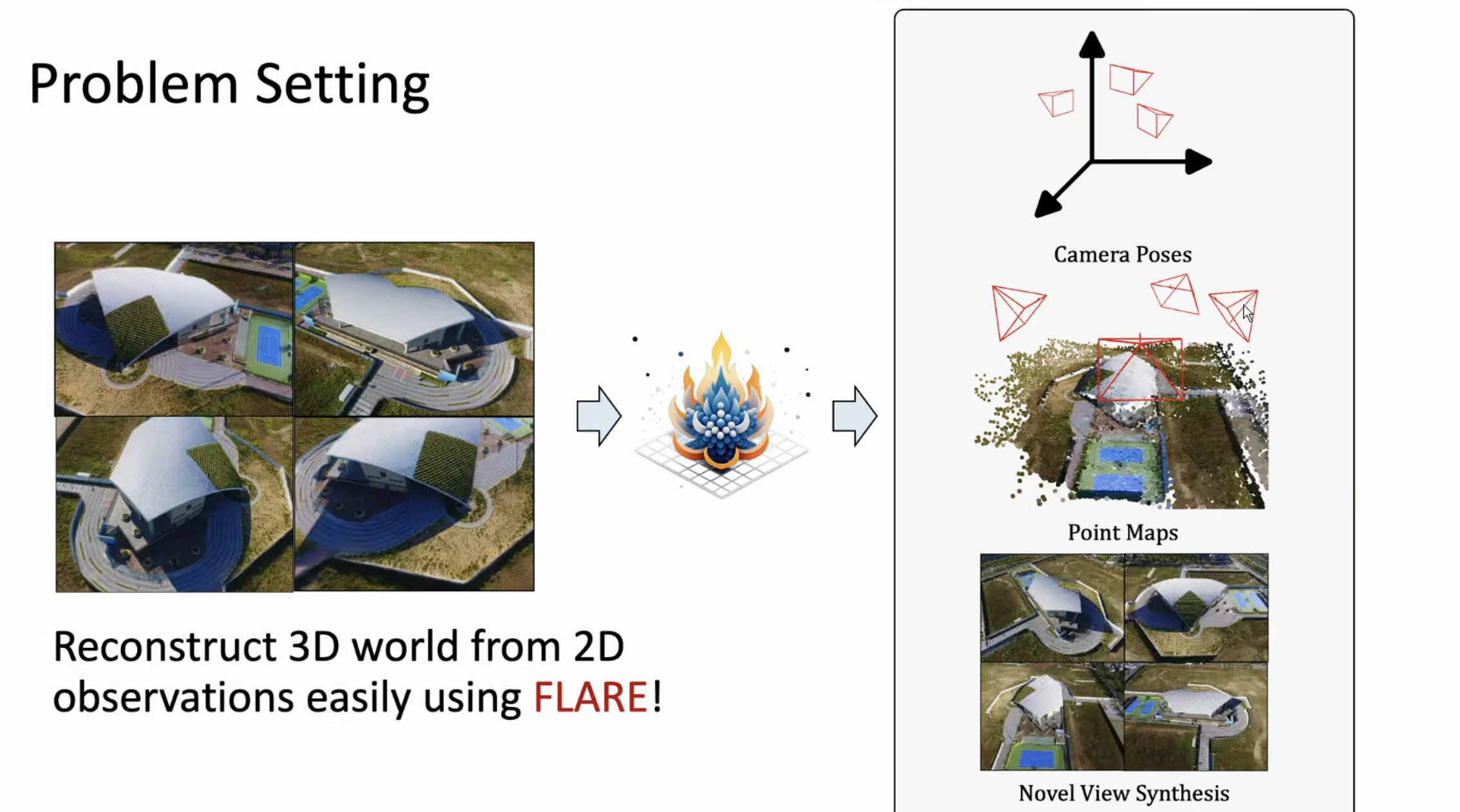
Problem Setting:infer high-quality camera poses and 3D geometry from uncalibrated sparse-view images (i.e., as few as 2-8 inputs), which is a challenging yet practical setting in real-world applications.
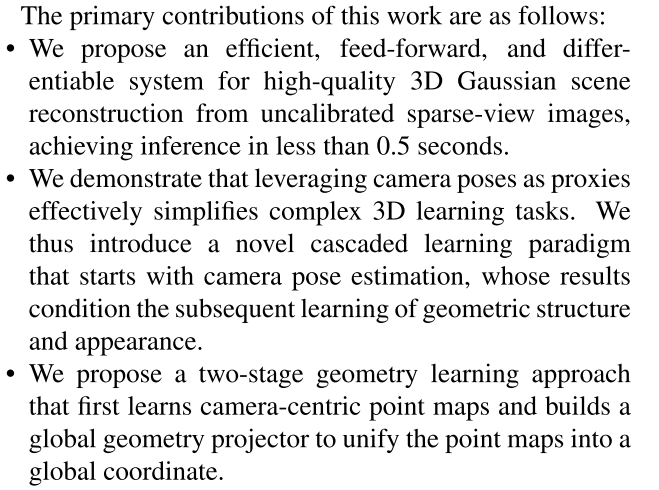
Primary Contributions:
Method
关键词:feed-forward model,cascaded learning paradigm
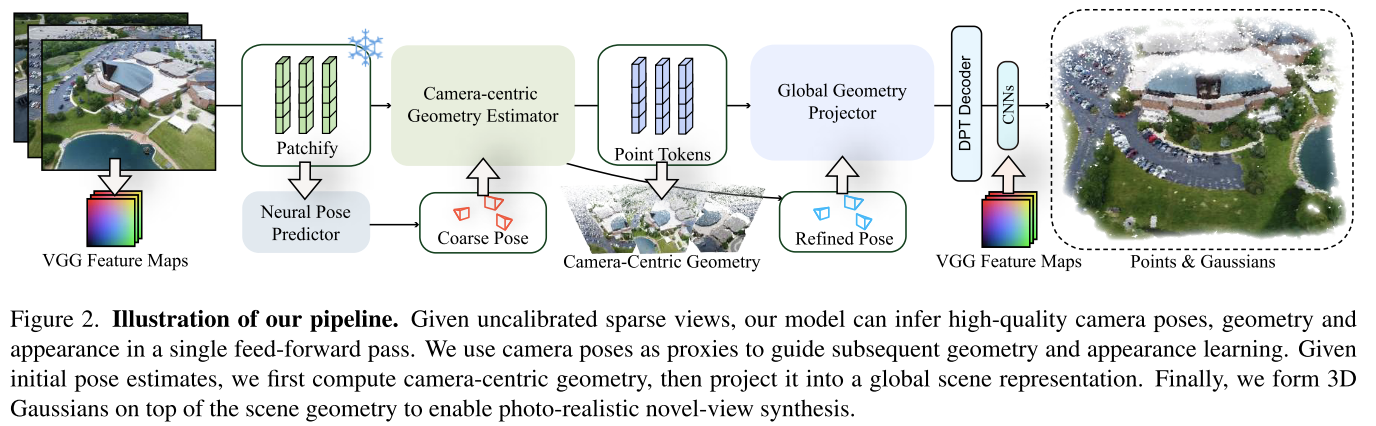
Neural Pose Predictor
受到posediffusion、vggsfm等工作的影响,这篇工作也放弃了feature matching,并且将位姿估计问题表述为image space to camera space的direct transformation问题,通过end-to-end transformer model来求解。
此处作者提到了一个重要的观察:We observe that the estimated poses do not need to be very accurate—only approximating the ground truth distribution is enough. This aligns with our key insight: camera poses, even imperfect, provide essential geometric priors and spatial initialization, which significantly reduces the complexity for geometry and appearance reconstruction.
即估计的pose不需要非常精确,只要能提供必要的几何先验和空间初始化,也能够降低几何和外观重建的复杂性。
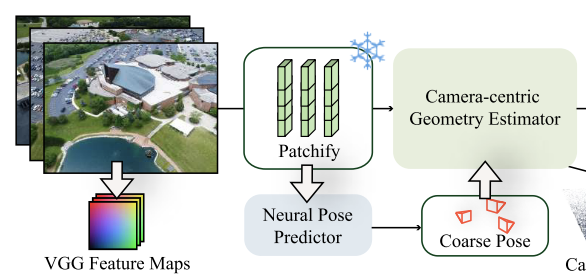
Multi-view Geometry Estimation
这部分的思路: Our key idea is to first learn camera-centric geometry in local frames (camera coordinate system) and then build a neural scene projector to transform it into a global world coordinate system with the guidance of estimated poses.
先学习局部的几何,之后再在pose的指导下转换到全局坐标系
疑问:既然已经有了FLARE这样的工作,pose可以指导网络来更好的重建。那么,给VGGT接上BA后处理的意义又在哪里呢?
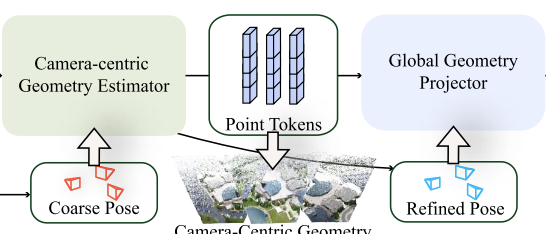
Camera-centric Geometry Estimation
image tokens + camera tokens输入,输出local point tokens和refined pose。
通过DPT-based decoder得到local dense point map和confidence map。
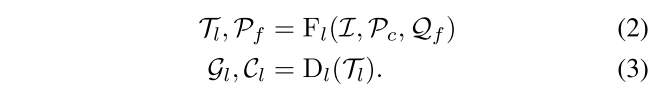
Global Geometry Projection
local point tokens和refined pose作为输入,输出global image tokens。
通过DPT-based decoder得到global dense point map和confidence map。
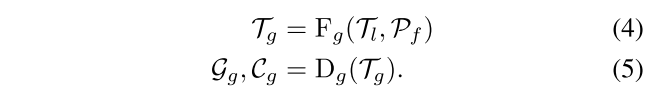
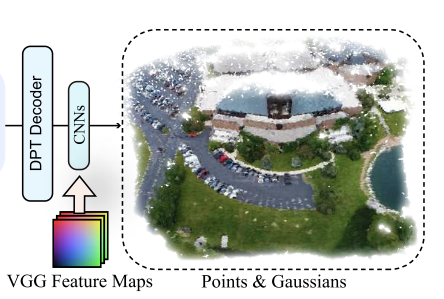
3D Gaussians for Appearance Modeling
类似于splatt3r,通过gaussian head来预测gaussian parameters。
Training Loss
由于这是一个joint learning framework,因此使用由camera pose loss、geometry loss、Gaussian Splatting loss组合成的multi-task loss来进行训练。
其中camera pose loss参考VGGSFM

而geometry loss类似dust3r


Gaussian Splatting loss如下所示,还包括了depth loss,用depth anything来估计depth
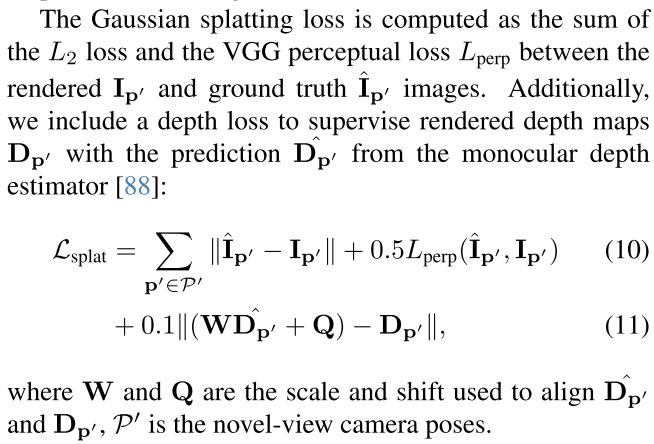
最终,total loss为

Experiment
模型使用8 views作为input(而VGGT是随机的views)。
其他的实验看论文吧。。。

使用camera centric,可以迫使网络去关注局部的几何,这样就不会过多关注global geometry。
上面w/o camera centric是同样的参数量训练一周的结果。
个人总结
我对网络估计coarse pose,再refine,之后把refine pose用于估计global scene的过程非常的感兴趣。
FLARE估计local geometry的思路,其实和VGGT估计depth不谋而合,这两个工作或许验证了一点:estimate pose & local geometry,再进行global reconstruction,效果可能会更好!
另外,已知的pose如何帮助网络更好的重建,是个人认为非常值得关注的问题。类似于prompt depth anything,其实也可以做一个prompt pose anything。或者,我们在VGGT的基础上,引入pose的指导,引入modern BA。