CS231A Lecture 6:Stereo Systems
Reading:
[HZ] Chapter: 9 “Epip. Geom. and the Fundam. Matrix Transf.”
[HZ] Chapter: 18 “N view computational methods”
[FP] Chapters: 7 “Stereopsis”
[FP] Chapters: 8 “Structure from Motion”
Rectification
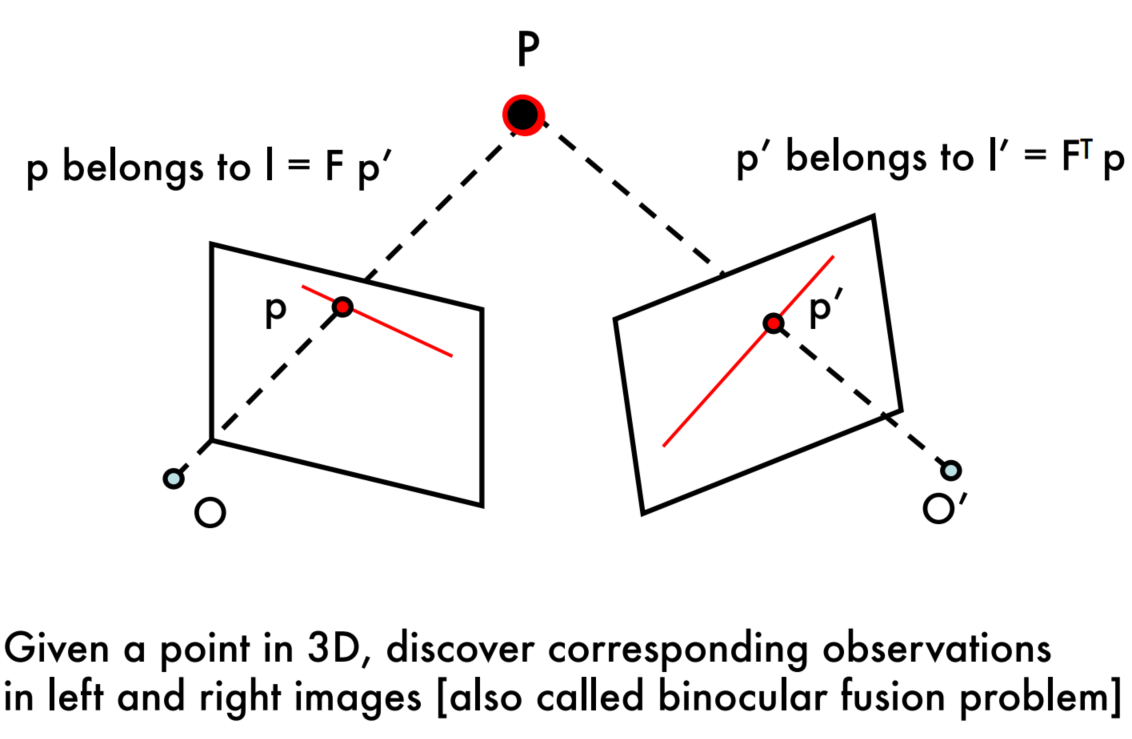
Epipolar geometry
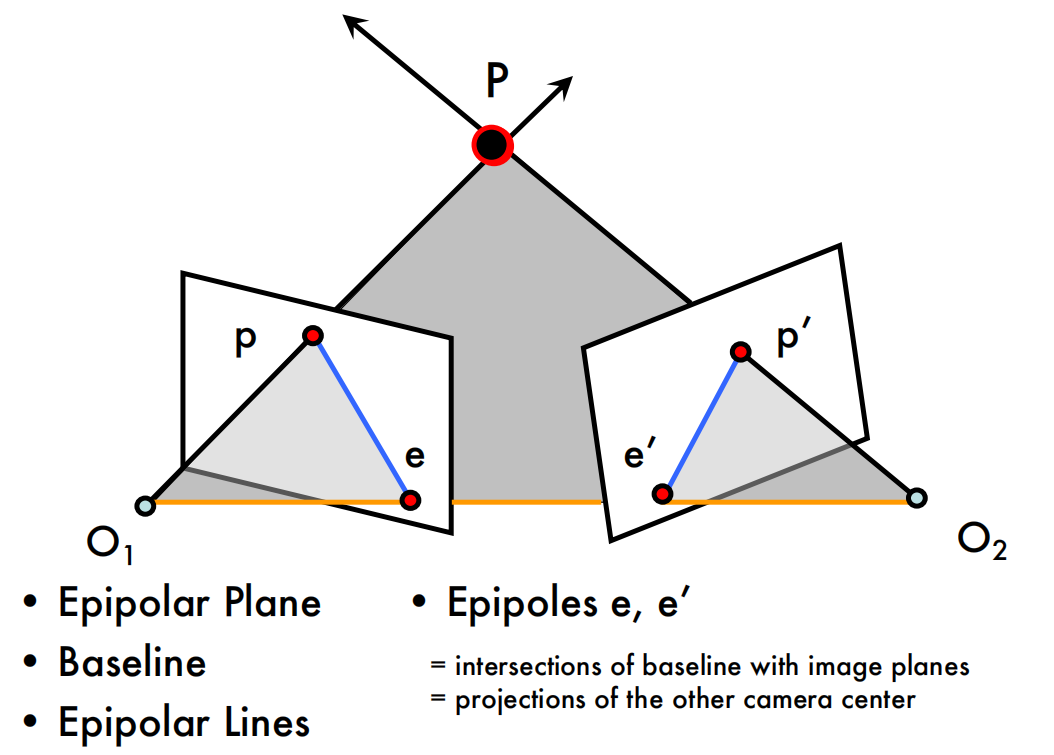
Epipolar Constraint
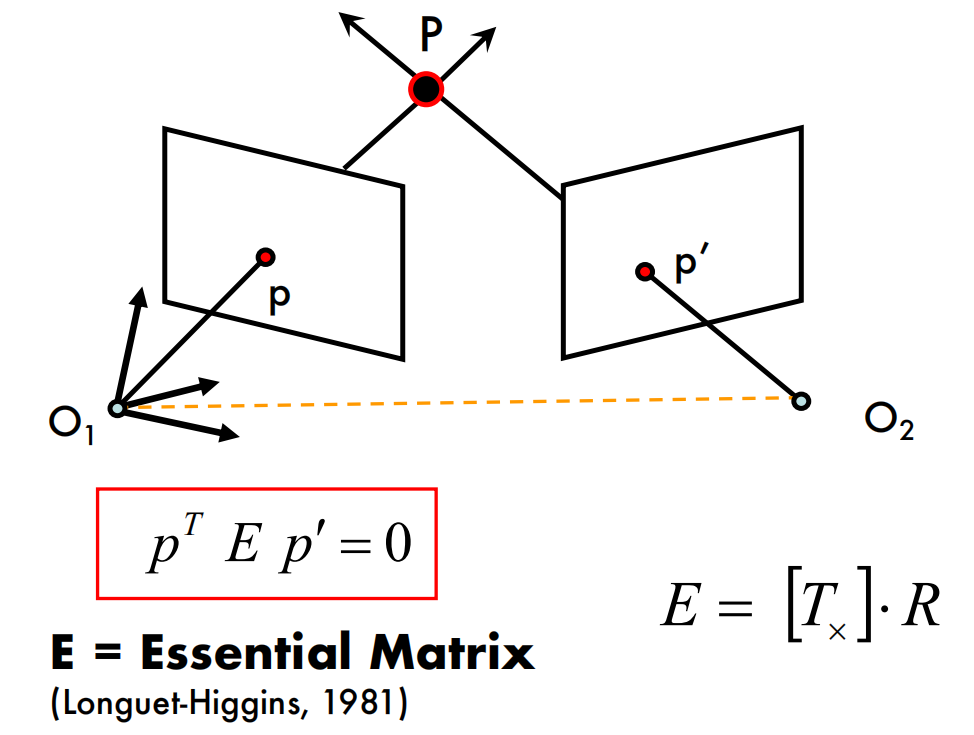
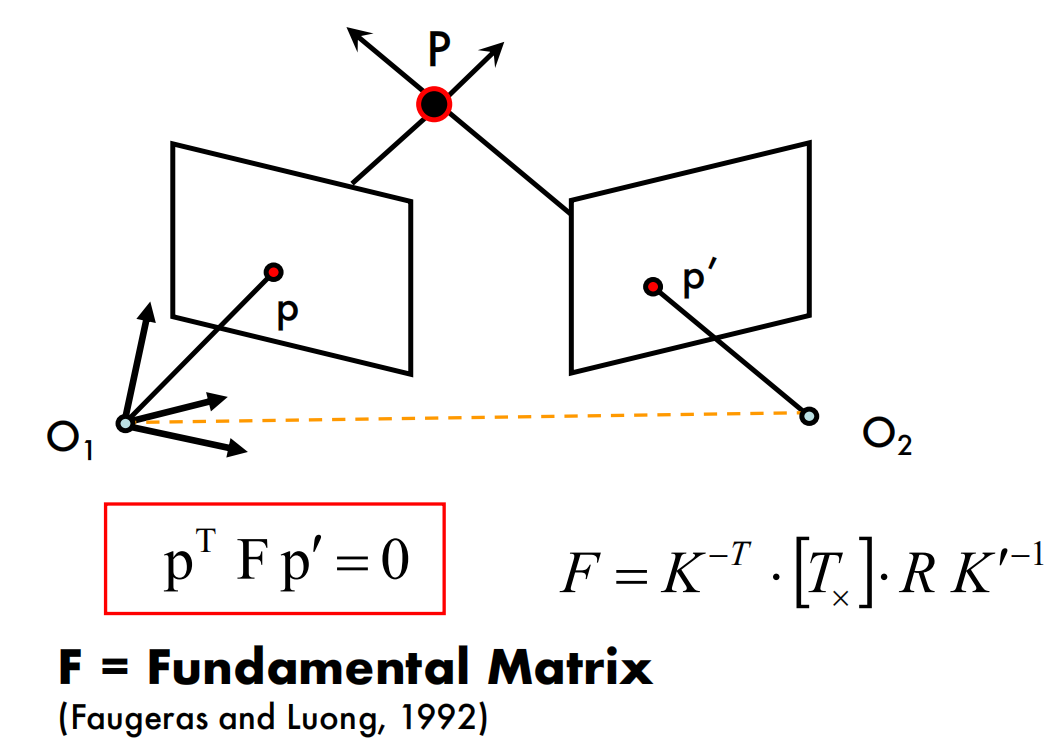
Parallel image planes
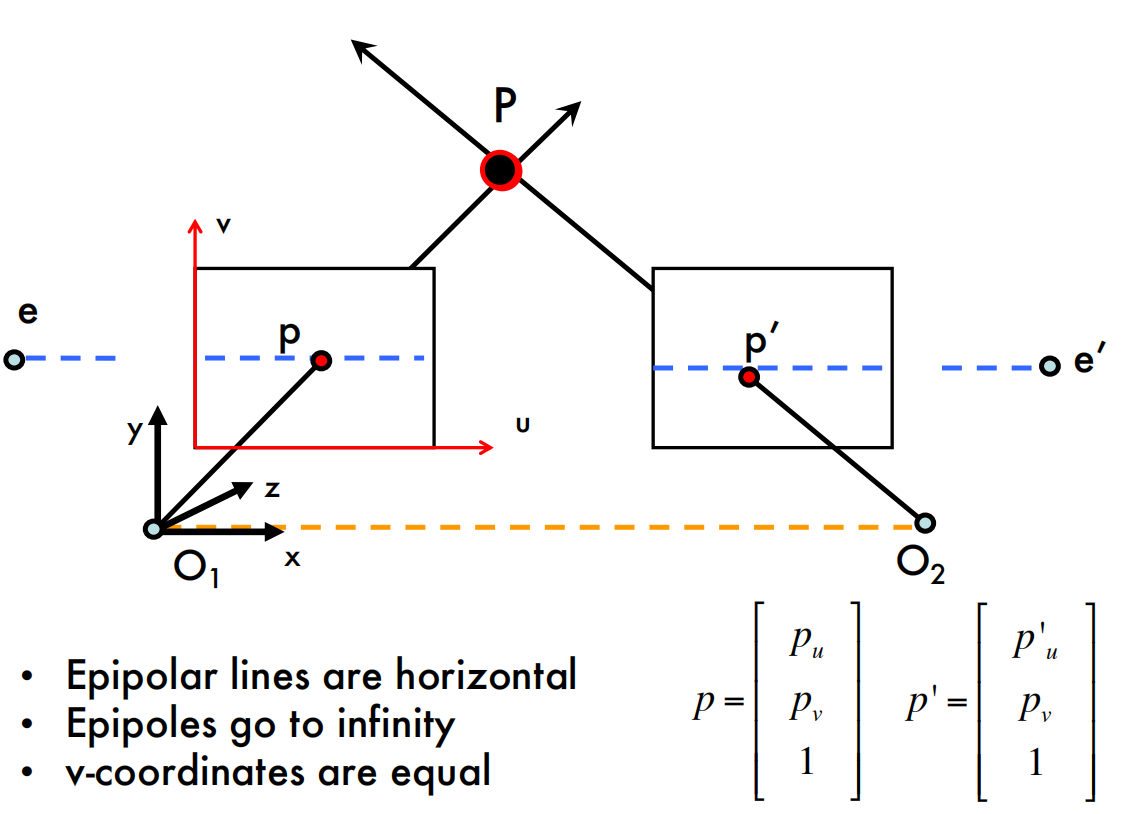
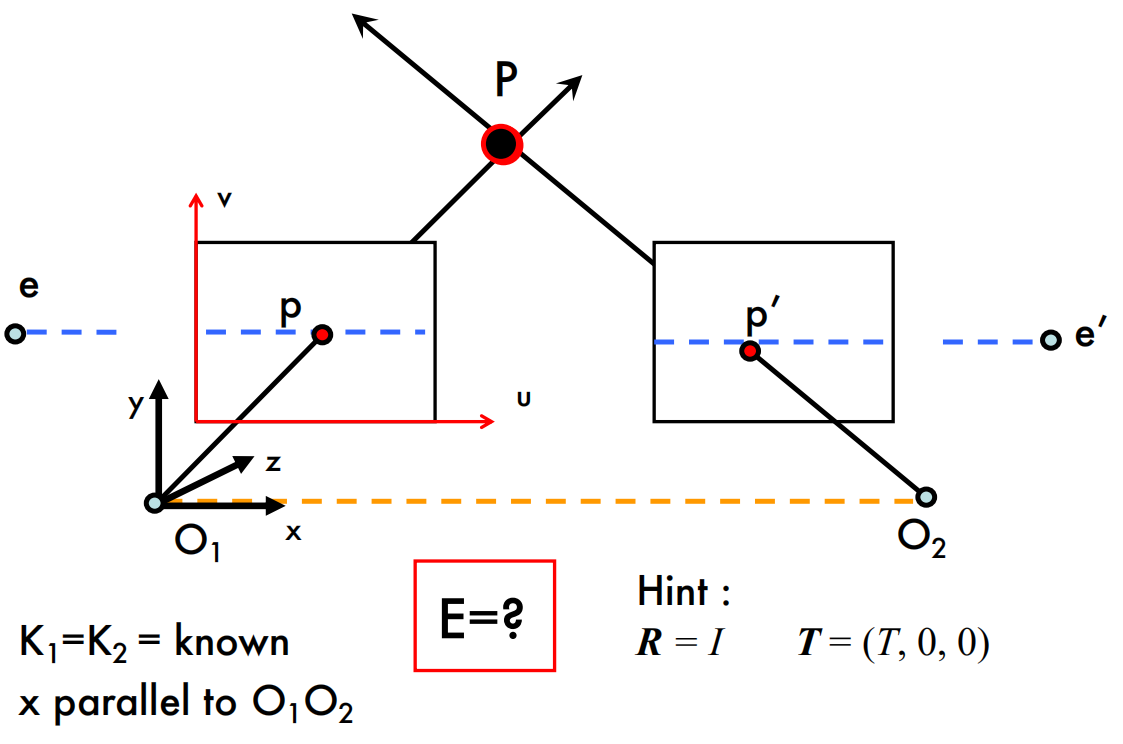
Essential matrix for parallel images
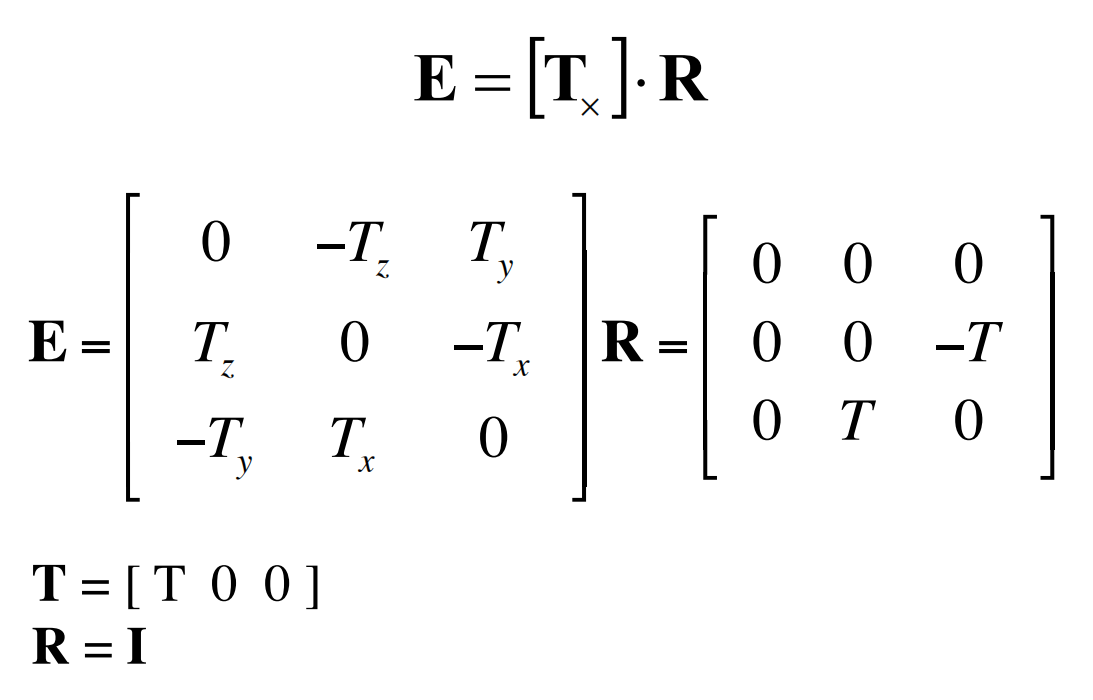
What are the directions of epipolar lines?
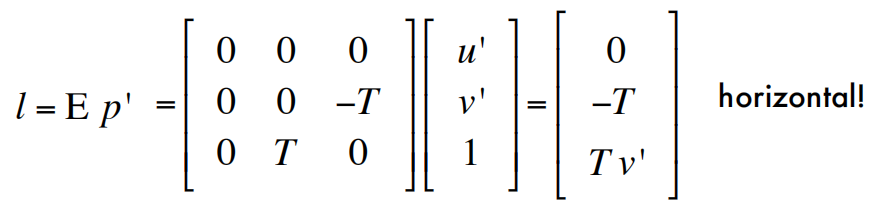
How are p and p’ related?
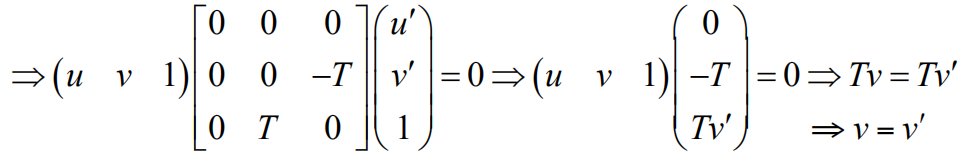
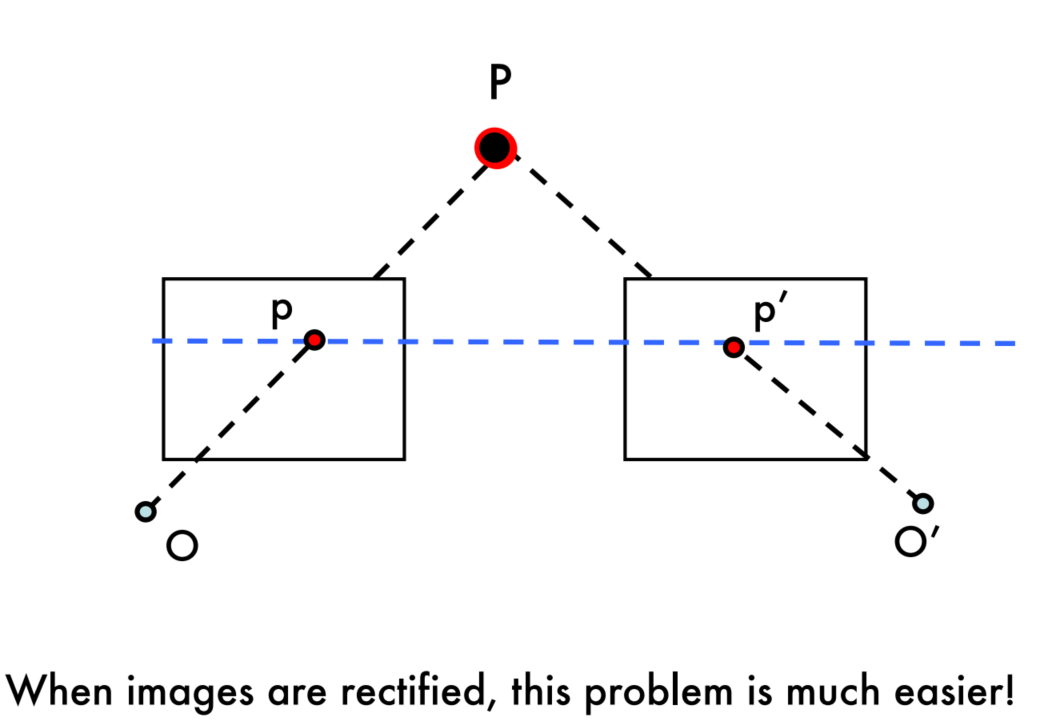
Rectification: making two images “parallel”
Rectification
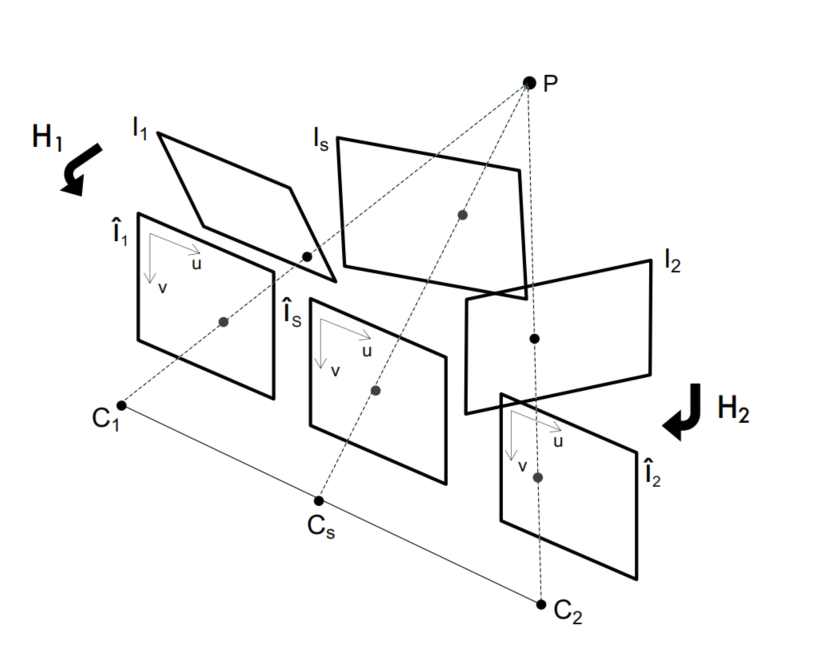
Example
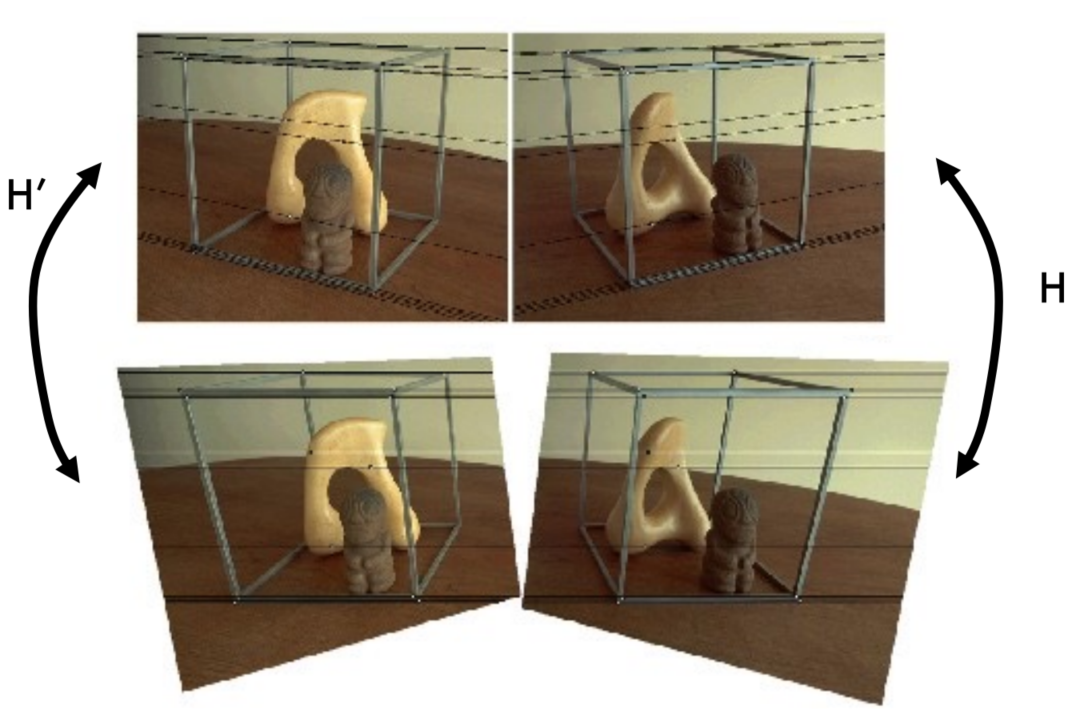

Why it is useful?
- Epipolar constraint $\rightarrow v = v’$
- New views can be synthesized by linear interpolation
Why are parallel images useful?
Makes triangulation easy
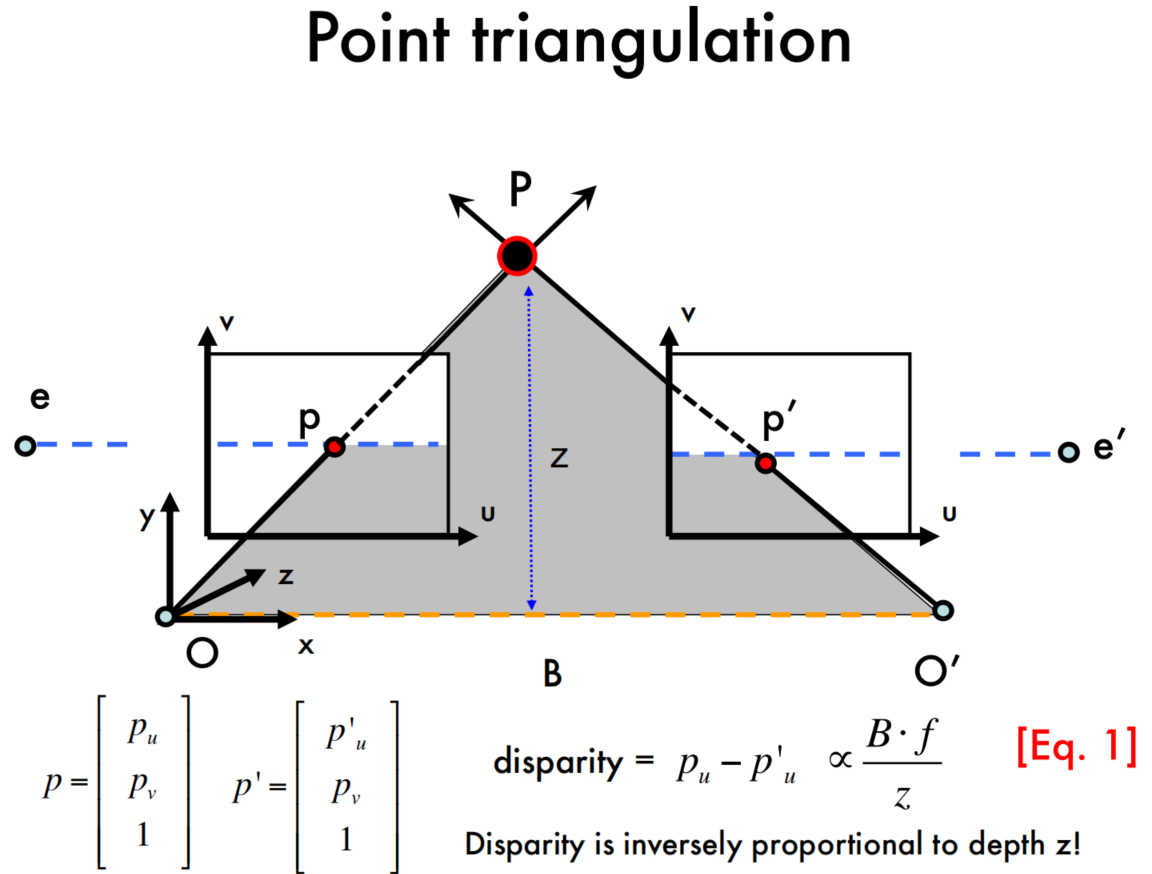
这里有点类似双目相机的模型了。
Makes the correspondence problem easier
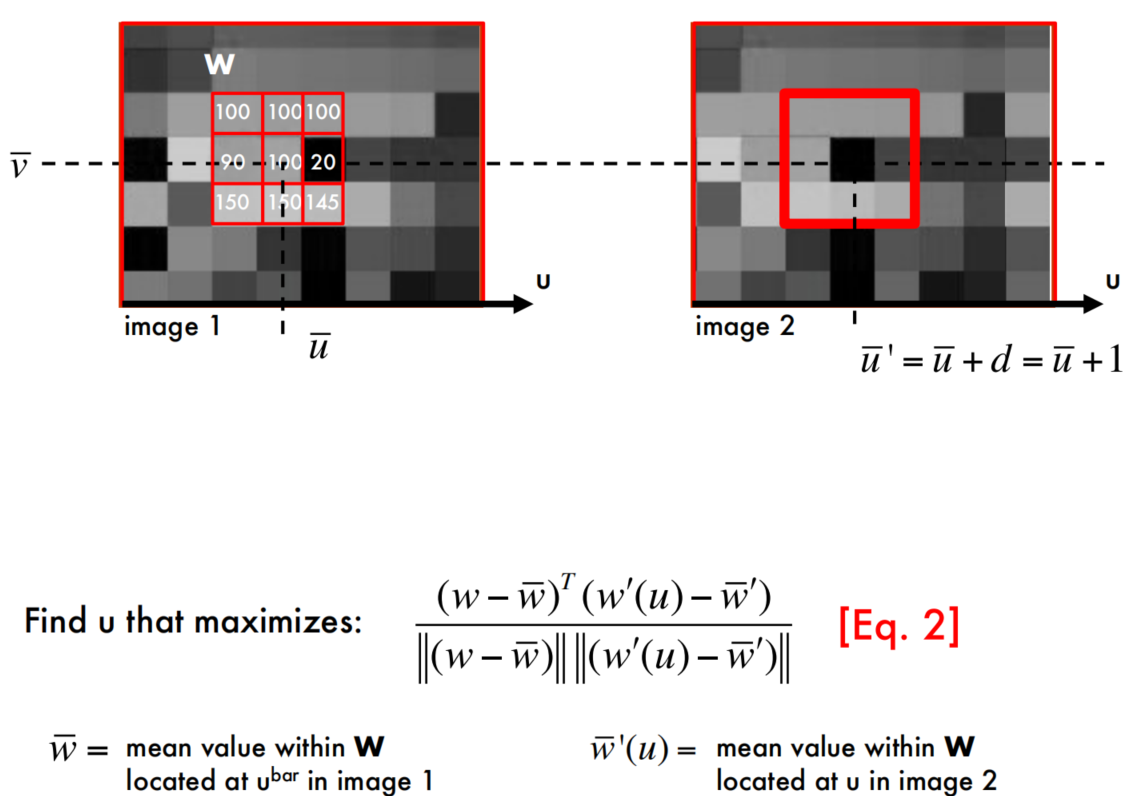
Correspondence problem
Correlation Methods
A Simple Idea
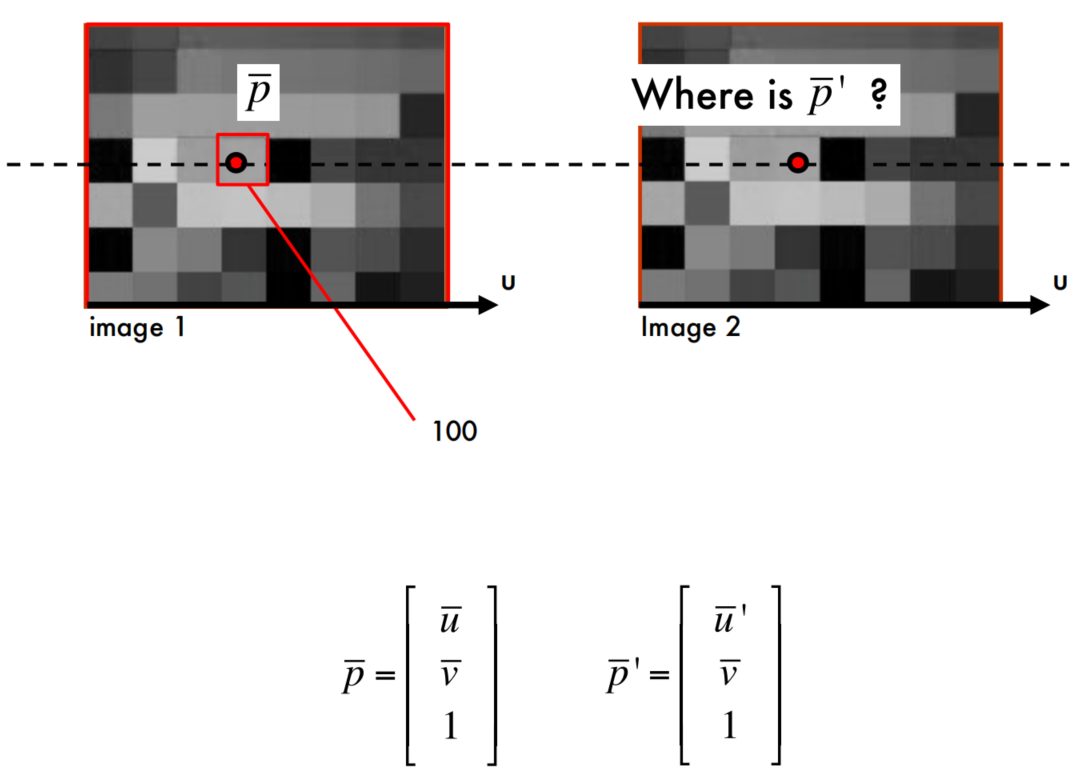
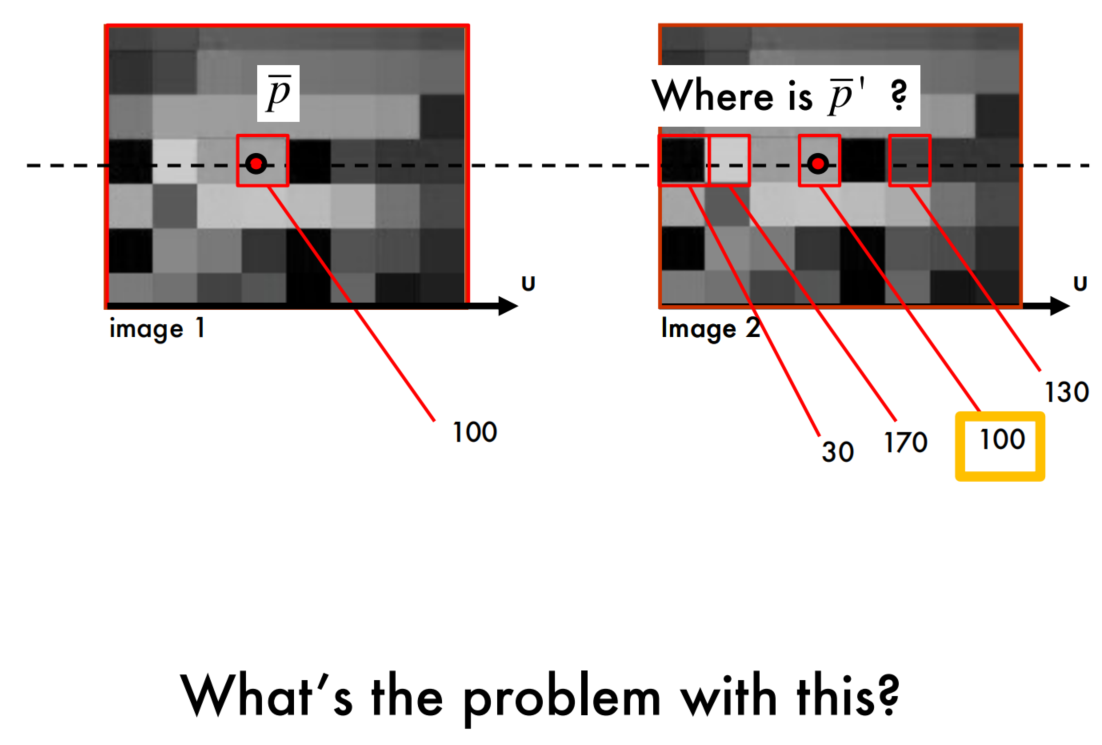
思考:
这里的问题是,只检查一个像素点,没有考虑到像素值相同的点可能比较多,很容易导致错误匹配。
Window-based correlation
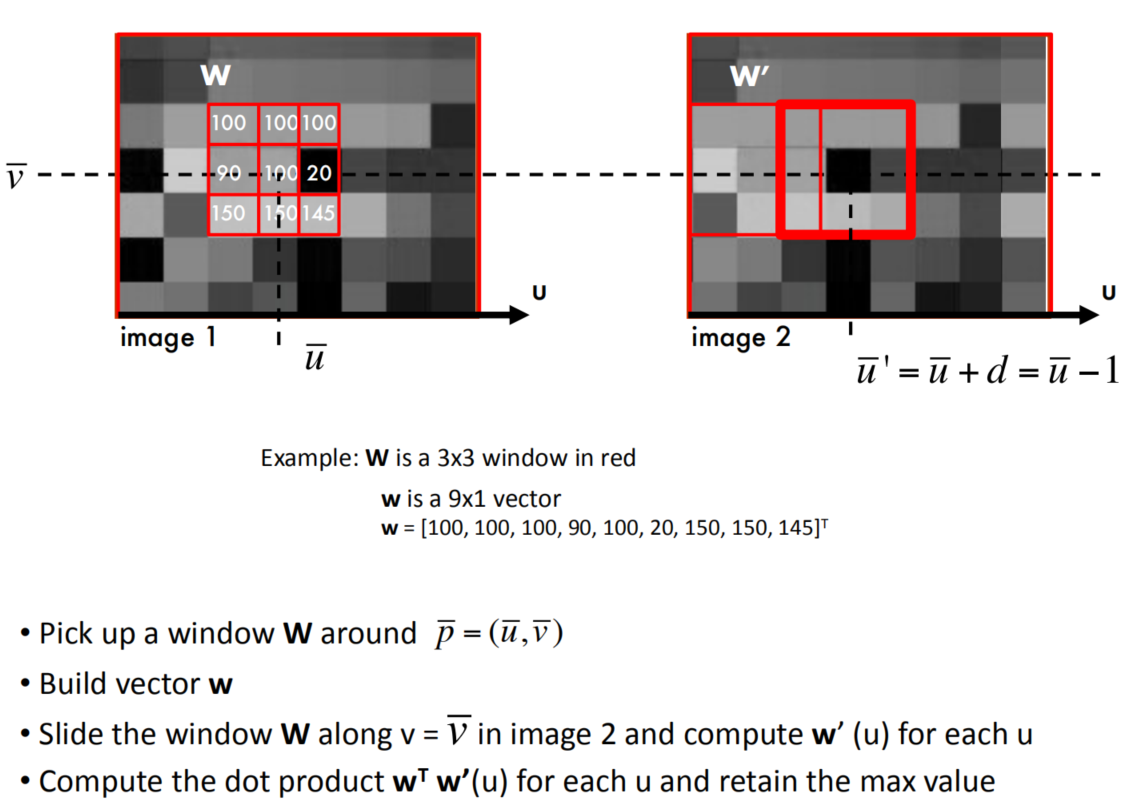
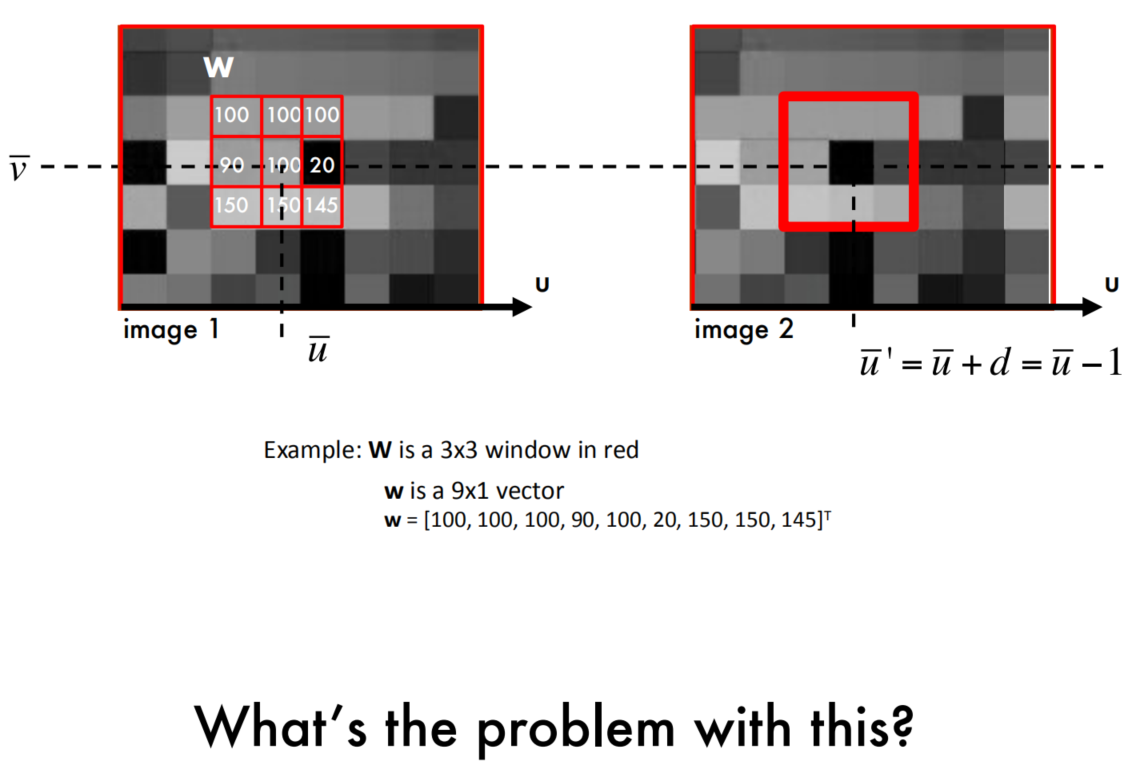
思考:
这里的问题是,只计算两个矩阵的点乘,并且认为最大值是匹配的最好的。
这样处理很容易受到光照或者曝光的影响,如下所示。
Changes of brightness/exposure

Normalized cross-correlation
Effect of the window’s size

Issues
Fore shortening effect
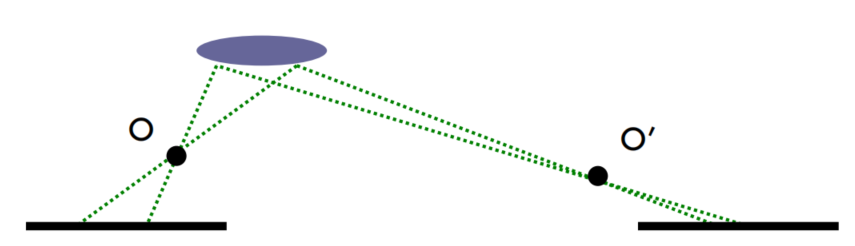
这个网站把Fore shortening effect介绍的非常清楚:Foreshortening – What It Means and How to Paint It
从上图中也可以看出,左边相机拍摄的物体很长,而右边因为距离较远就缩短了。前面几种算法在这里容易出问题,他们都是在一条水平线上查找固定大小的window,但是利用图像金字塔应该可以处理这种问题。
Occlusions
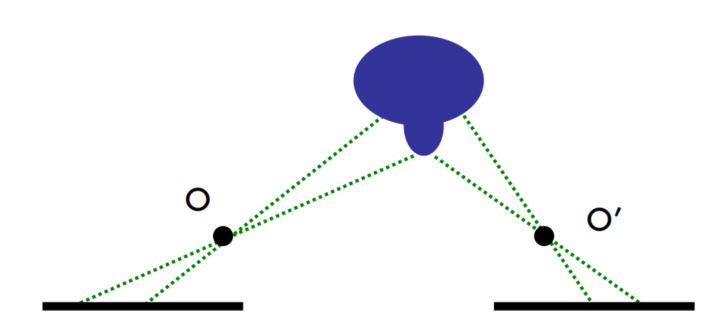
因为遮挡导致两个相机观察的内容不一样。
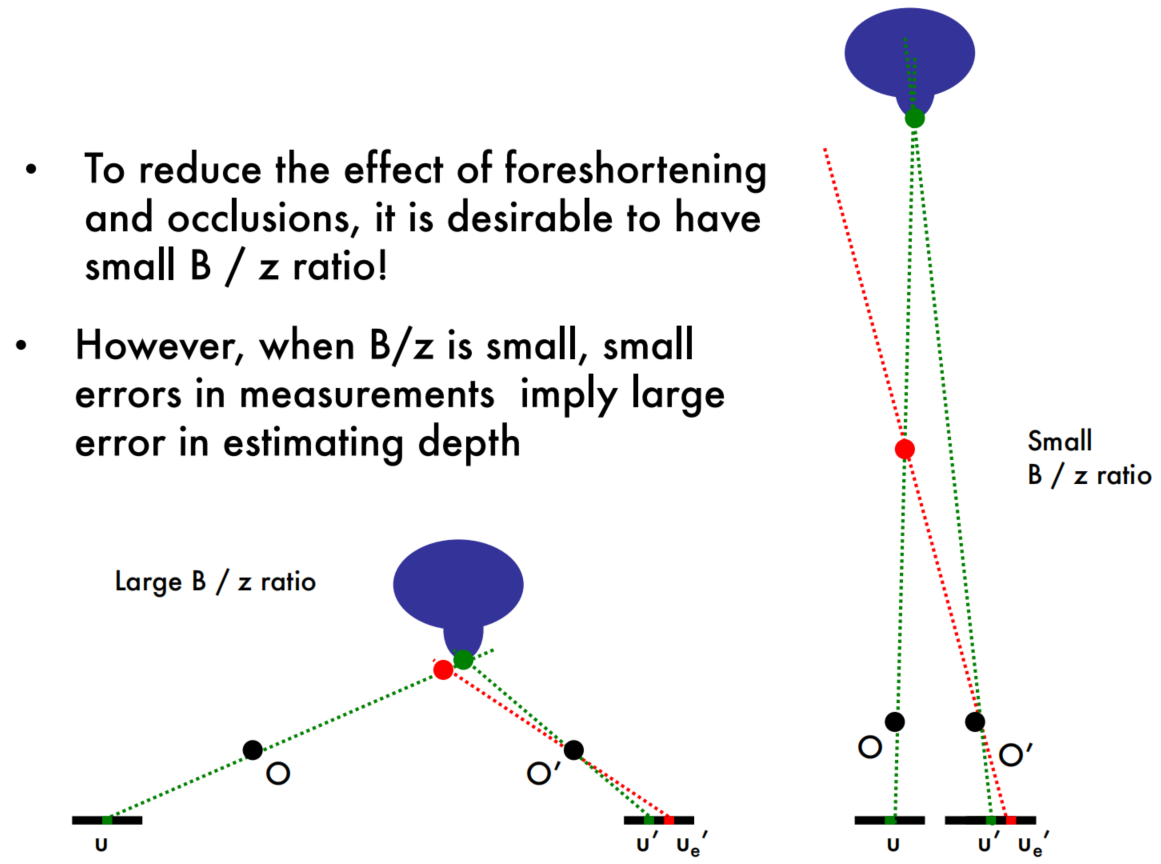
Base line trade-off
Homogeneous regions
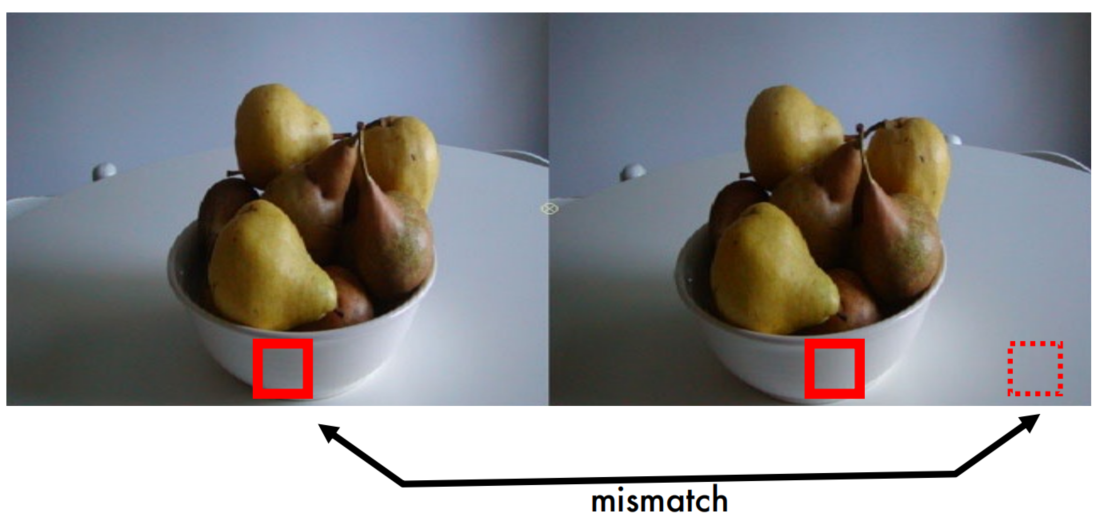
Repetitive patterns
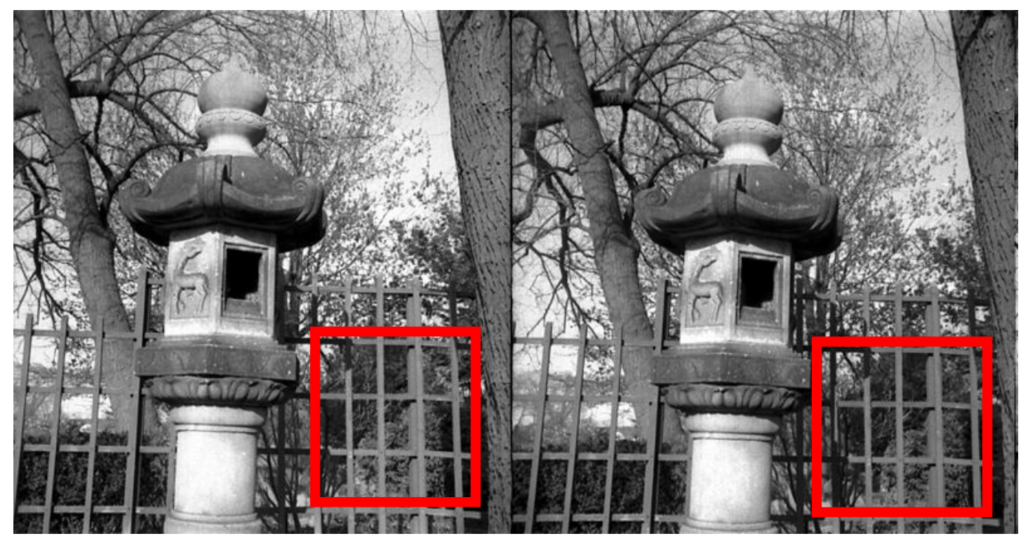

Correspondence problem is difficult!

Non-local constraints




